Freshwater Wildlife, Freshwater Habitat Facts, And Animals live in freshwater
Freshwater wildlife, residing in the heart of aquatic ecosystems, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the delicate balance of nature. As we delve into the intricacies of these habitats, it becomes evident that they are not just bodies of water but thriving communities supporting a vast array of life.
Rivers and Streams
Rivers and streams, flowing veins of freshwater ecosystems, host a dynamic environment. From darting fish to intricate plant life along the banks, these habitats showcase nature’s resilience.
Lakes and Ponds
Lakes and ponds, serene and reflective, are home to a different set of species. Exploring the depths, we uncover the mysteries of aquatic life beneath the calm surface.
Wetlands
Wetlands, often overlooked, serve as nurseries for many species. These transitional zones are crucial for the survival of amphibians and diverse bird populations.
Freshwater Species
- Fish Species
- Amphibians and Reptiles
- Invertebrates
1- Fish Species
The underwater world is teeming with fish diversity. From sleek predators to schooling species, each plays a unique role in the aquatic tapestry. Freshwater Fish Species.
- Salmon Fish
- Trout Fish
- Bass Fish
- Catfish
A- Salmon Fish
They are born in freshwater streams & where they spend the early stages of their lives. As they mature, a profound instinct drives them to migrate towards the open sea. This migration is not just a journey; it’s a critical part of their life cycle.

B- Trout Fish
Trout encompass various species, each adapted to specific environmental conditions. Common species include rainbow trout, brown trout, and brook trout, each displaying unique characteristics and behaviors.
Trout thrive in cool, well-oxygenated waters, often found in mountain streams, rivers, and lakes. Their preference for pristine environments makes them indicators of water quality.
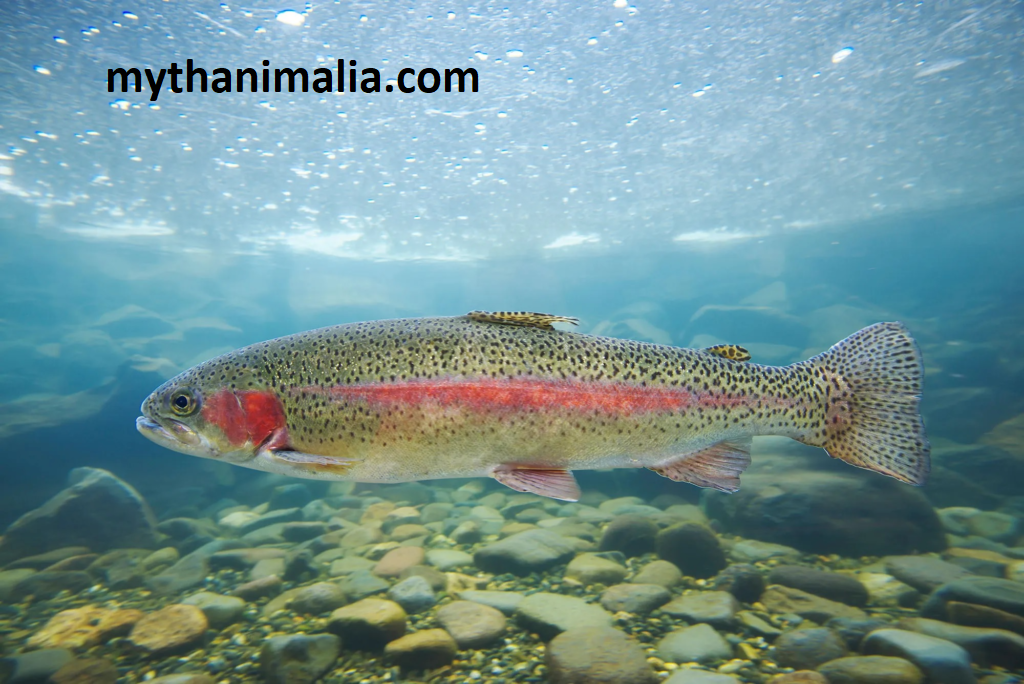

C- Bass Fish
Known for their distinctive large mouths and aggressive feeding behavior, large-mouth bass are a favorite among anglers. They often inhabit slow-moving or still waters with abundant cover. Smaller but no less spirited, small-mouth bass prefer clearer, swifter waters. Their bronze-colored bodies and feisty nature make them a sought-after catch for anglers.
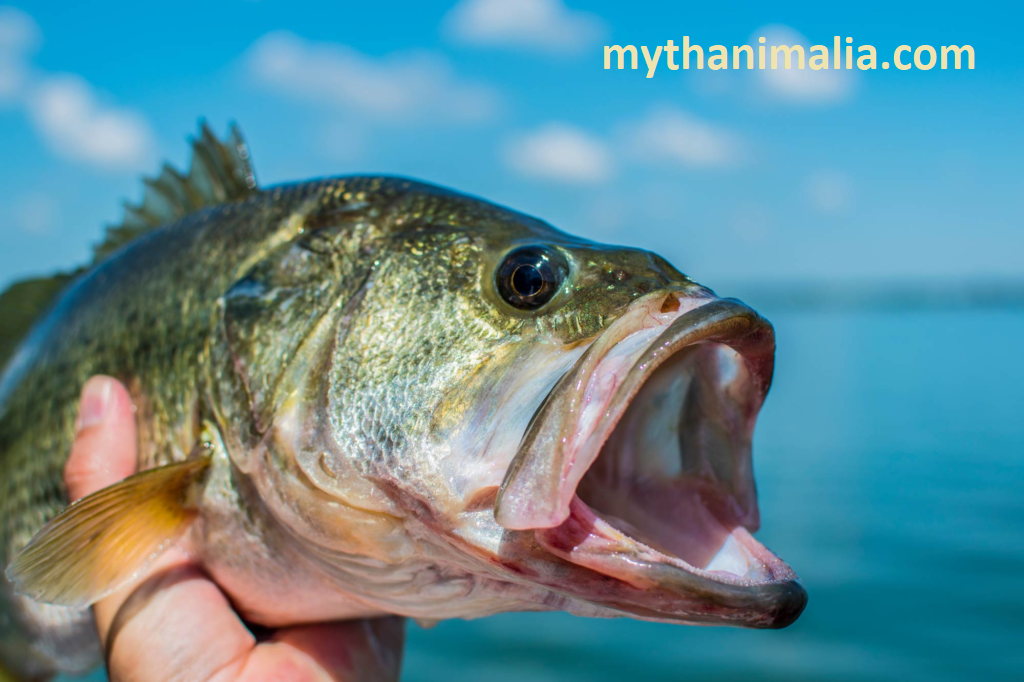

D- Catfish
Catfish, with their distinctive whisker-like barbels and bottom-dwelling habits, bring a unique charm to freshwater ecosystems.
Channel catfish, known for their smooth skin and deeply forked tails, are prevalent in freshwater bodies across North America. They are prized by anglers for their size and delicious flesh.

2- Amphibians and Reptiles
Adapting to both aquatic and terrestrial life, amphibians and reptiles bring a fascinating dimension to freshwater ecosystems.
3- Invertebrates
From microscopic invertebrates to larger crayfish, the variety of invertebrates in freshwater habitats forms the backbone of the ecosystem.
Adaptations of Freshwater Wildlife
- Physiological Adaptations
- Behavioral Adaptations
A- Physiological Adaptations
Freshwater species have evolved unique physiological features to thrive in environments with varying temperatures, oxygen levels, and salinity.
B- Behavioral Adaptations
Observing the behaviors of freshwater wildlife reveals survival strategies, mating rituals, and intricate social dynamics within these communities.
Threats to Freshwater Wildlife
- Pollution
- Habitat Destruction
- Climate Change
- Conservation Efforts
1- Pollution
The menace of pollution casts a dark shadow over freshwater habitats. Chemical contaminants and plastic waste jeopardize the health of aquatic life.
2- Habitat Destruction
As human development expands, the natural habitats of freshwater species face destruction, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
3- Climate Change
The ripple effects of climate change impact freshwater ecosystems, altering water temperatures, precipitation patterns, and habitat distribution.
4- Conservation Efforts
Recognizing the urgency of conservation, organizations worldwide work tirelessly to preserve freshwater habitats and protect the species within them.
Which animals live in freshwater
Fish living in freshwater habitats have plenty of company. Snails, worms, turtles, frogs, marsh birds, mollusks, alligators, beavers, otters, snakes, and many types of insects live there too. Some unusual animals, like the river dolphin and the diving bell spider, are freshwater creatures.
Human Impact on Freshwater Ecosystems
- Sustainable Practices
- Responsible Tourism
- The Role of Freshwater Wildlife in the Food Chain
A- Sustainable Practices
Adopting sustainable practices in agriculture, industry, and daily life is crucial to minimizing our impact on freshwater ecosystems.
B- Responsible Tourism
Tourism can coexist with conservation when managed responsibly. Educating visitors about the importance of preserving these habitats is essential.
C- The Role of Freshwater Wildlife in the Food Chain
Understanding the intricate web of predator-prey relationships highlights the significance of each species in maintaining a healthy and balanced ecosystem.
Case Studies from Different Continents
Exploring unique species from various continents showcases the rich tapestry of freshwater life, emphasizing the need for global conservation efforts.
Research Limitations
Studying underwater environments presents challenges, from limited visibility to the complexity of tracking elusive species.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in technology, such as underwater drones and environmental DNA analysis, open new avenues for studying and understanding freshwater ecosystems.
Importance of Awareness
Raising awareness about freshwater conservation is essential. Educational initiatives empower communities to take an active role in protecting local water bodies.
Involvement of Schools and Communities
Incorporating freshwater education into school curricula and community programs fosters a sense of responsibility and appreciation for these vital ecosystems.
Benefits of Freshwater Wildlife to Humans
- Economic Importance
- Cultural Significance
1- Economic Importance
Freshwater ecosystems contribute significantly to economies through fisheries, recreation, and tourism.
2- Cultural Significance
Many cultures have deep-rooted connections to freshwater habitats, reflected in traditions, folklore, and spiritual beliefs.
Sustainable Practices
Striking a balance between human needs and environmental preservation requires adopting sustainable practices in resource management.
Community Engagement
Communities are integral to successful conservation efforts. Engaging with residents ensures a holistic approach to freshwater conservation.
Future Outlook for Freshwater Wildlife
- Emerging Threats
- Potential Solutions
1- Emerging Threats
Anticipating and addressing emerging threats, such as invasive species and emerging pollutants, is vital for the future health of freshwater ecosystems.
2- Potential Solutions
Innovative solutions, including habitat restoration, sustainable resource management, and international collaboration, offer hope for the future of freshwater wildlife.
FAQ’s
Q1- What is Freshwater Wildlife?
A1- Freshwater wildlife refers to the diverse range of plants, animals, and microorganisms inhabiting aquatic environments with low salinity, such as rivers, lakes, and ponds.
Q2- Why is Freshwater Biodiversity Important?
A2- Freshwater biodiversity is crucial as it supports ecosystem services, including water purification, nutrient cycling, and flood control. Additionally, diverse freshwater ecosystems contribute to the overall health of the planet.
Q3- How Does Pollution Affect Freshwater Wildlife?
A3- Pollution negatively impacts freshwater wildlife by degrading water quality, disrupting food chains, and causing habitat destruction. Species relying on these habitats suffer from the toxic effects of pollutants.
Q4- What is Habitat Destruction in Freshwater Environments?
A4- Habitat destruction in freshwater environments involves the alteration or degradation of natural habitats, primarily due to human activities like dam construction, deforestation, and urban expansion. This leads to the loss of critical habitats for many freshwater species.
Q5- How Can Individuals Contribute to Freshwater Wildlife Conservation?
A5- Individuals can contribute by adopting sustainable practices, reducing water pollution, supporting conservation organizations, and participating in local community initiatives aimed at preserving freshwater habitats.